Vectorize Moving Window Grid Operations on NumPy Arrays
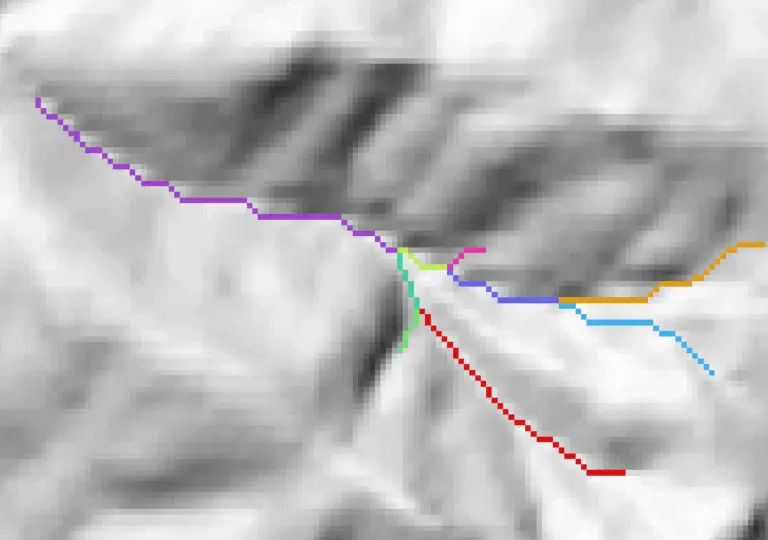
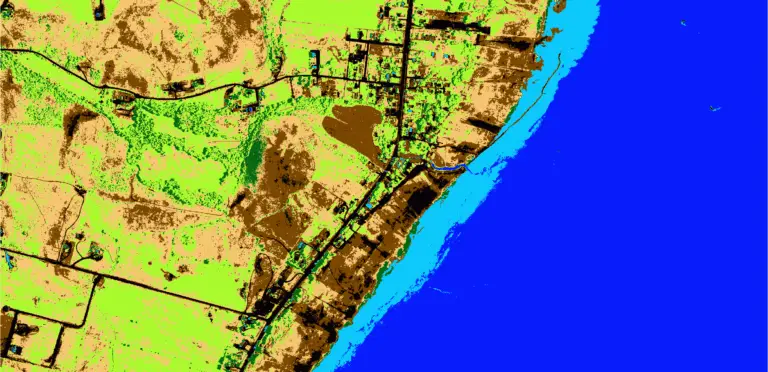
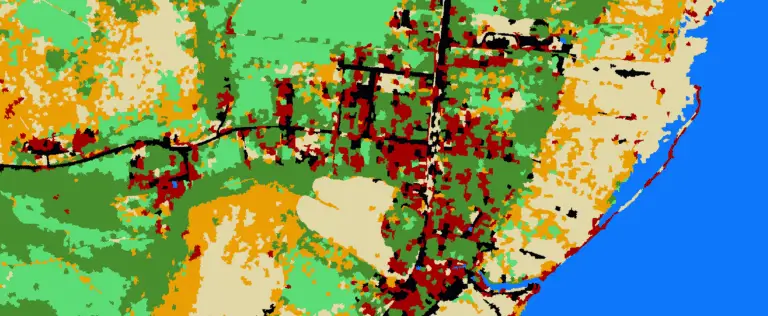
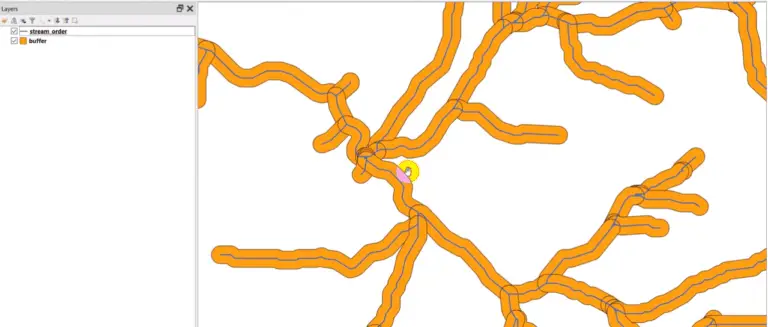
There’s a good chance you’ve done something today that used a sliding window (also known as a moving window) and you didn’t even know it. Have you done any photo editing? Many editing algorithms are based on moving windows. Do you do terrain analysis in GIS? Most topographic raster metrics (slope, aspect, hillshade, etc.) are…