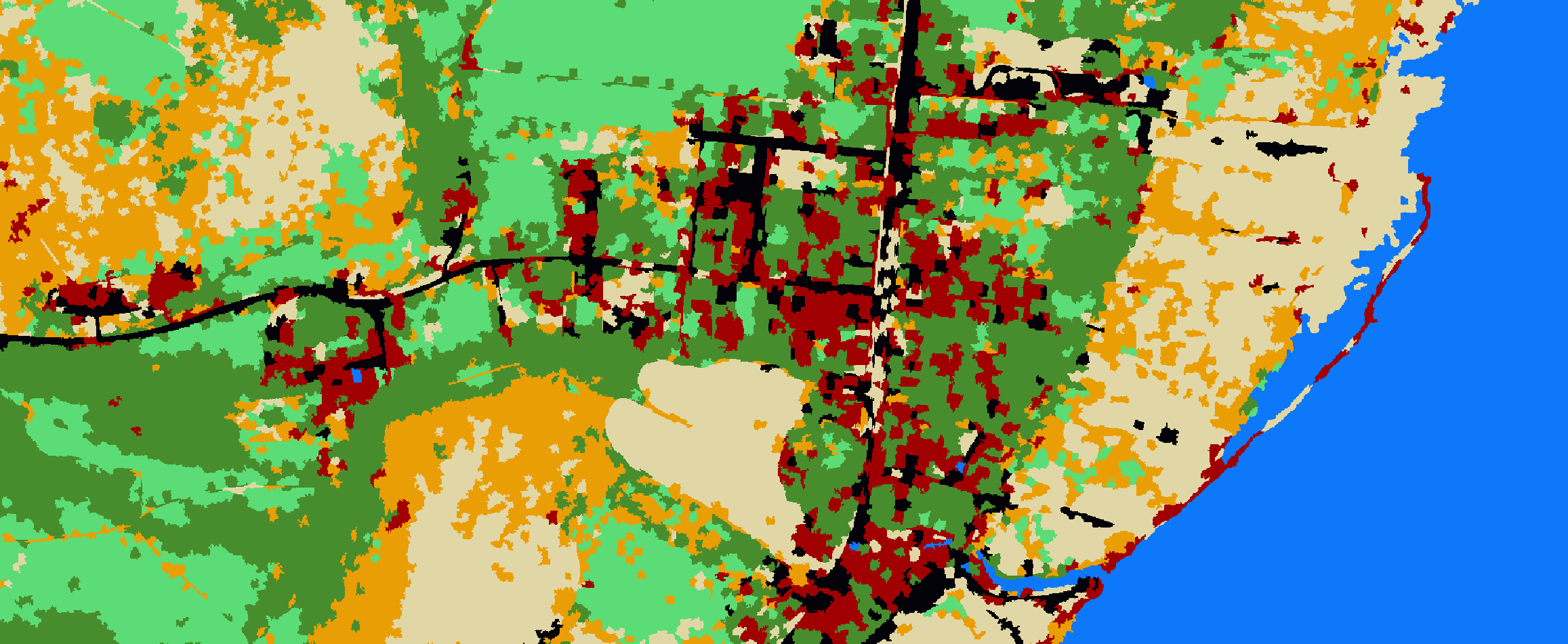
Python: Geographic Object-Based Image Analysis (GeOBIA) – Part 2: Image Classification
Use the random forests algorithm to classify image segments into land cover categories. This post is a continuation of Geographic Object-Based Image Analysis (GeOBIA). Herein, we use data describing land cover types to train and test the accuracy of a random forests classifier. Land cover data were created in the previous post. Step-be-step video instructions for the entire classification process are available from this YouTube playlist.
Create Training and Test Data Sets
import numpy as np
import geopandas as gpd
import pandas as pd
# read shapefile to geopandas geodataframe
gdf = gpd.read_file('C:/temp/naip/truth_data_subset_utm12.shp')
# get names of land cover classes/labels
class_names = gdf['label'].unique()
print('class names', class_names)
# create a unique id (integer) for each land cover class/label
class_ids = np.arange(class_names.size) + 1
print('class ids', class_ids)
# create a pandas data frame of the labels and ids and save to csv
df = pd.DataFrame({'label': class_names, 'id': class_ids})
df.to_csv('C:/temp/naip/class_lookup.csv')
print('gdf without ids', gdf.head())
# add a new column to geodatafame with the id for each class/label
gdf['id'] = gdf['label'].map(dict(zip(class_names, class_ids)))
print('gdf with ids', gdf.head())
# split the truth data into training and test data sets and save each to a new shapefile
gdf_train = gdf.sample(frac=0.7)
gdf_test = gdf.drop(gdf_train.index)
print('gdf shape', gdf.shape, 'training shape', gdf_train.shape, 'test', gdf_test.shape)
gdf_train.to_file('C:/temp/naip/train.shp')
gdf_test.to_file('C:/temp/naip/test.shp')
Rasterize Training Data
Paste the highlighted lines at the end of the obia.py file created during image segmentation. Code (obia.py) from Part 1 of the tutorial can be accessed at this link: https://opensourceoptions.com/blog/python-geographic-object-based-image-analysis-geobia/
import gdal
import ogr
# open NAIP image as a gdal raster dataset
naip_fn = 'C:/temp/naip/clipped.tif'
naip_ds = gdal.Open(naip_fn)
# open the points file to use for training data
train_fn = 'C:/temp/naip/train.shp'
train_ds = ogr.Open(train_fn)
lyr = train_ds.GetLayer()
# create a new raster layer in memory
driver = gdal.GetDriverByName('MEM')
target_ds = driver.Create('', naip_ds.RasterXSize, naip_ds.RasterYSize, 1, gdal.GDT_UInt16)
target_ds.SetGeoTransform(naip_ds.GetGeoTransform())
target_ds.SetProjection(naip_ds.GetProjection())
# rasterize the training points
options = ['ATTRIBUTE=id']
gdal.RasterizeLayer(target_ds, [1], lyr, options=options)
# retrieve the rasterized data and print basic stats
data = target_ds.GetRasterBand(1).ReadAsArray()
print('min', data.min(), 'max', data.max(), 'mean', data.mean())
Get segments representing each land cover classification type and ensure no segment represents more than one class.
ground_truth = target_ds.GetRasterBand(1).ReadAsArray()
classes = np.unique(ground_truth)[1:]
print('class values', classes)
segments_per_class = {}
for klass in classes:
segments_of_class = segments[ground_truth == klass]
segments_per_class[klass] = set(segments_of_class)
print("Training segments for class", klass, ":", len(segments_of_class))
intersection = set()
accum = set()
for class_segments in segments_per_class.values():
intersection |= accum.intersection(class_segments)
accum |= class_segments
assert len(intersection) == 0, "Segment(s) represent multiple classes"
Classify the image
train_img = np.copy(segments)
threshold = train_img.max() + 1
for klass in classes:
class_label = threshold + klass
for segment_id in segments_per_class[klass]:
train_img[train_img == segment_id] = class_label
train_img[train_img <= threshold] = 0
train_img[train_img > threshold] -= threshold
training_objects = []
training_labels = []
for klass in classes:
class_train_object = [v for i, v in enumerate(objects) if segment_ids[i] in segments_per_class[klass]]
training_labels += [klass] * len(class_train_object)
training_objects += class_train_object
print('Training objects for class', klass, ':', len(class_train_object))
classifier = RandomForestClassifier(n_jobs=-1)
classifier.fit(training_objects, training_labels)
print('Fitting Random Forest Classifier')
predicted = classifier.predict(objects)
print('Predicting Classifications')
clf = np.copy(segments)
for segment_id, klass in zip(segment_ids, predicted):
clf[clf == segment_id] = klass
print('Prediction applied to numpy array')
mask = np.sum(img, axis=2)
mask[mask > 0.0] = 1.0
mask[mask == 0.0] = -1.0
clf = np.multiply(clf, mask)
clf[clf < 0] = -9999.0
print('Saving classificaiton to raster with gdal')
clfds = driverTiff.Create('C:/temp/naip/classified.tif', naip_ds.RasterXSize, naip_ds.RasterYSize,
1, gdal.GDT_Float32)
clfds.SetGeoTransform(naip_ds.GetGeoTransform())
clfds.SetProjection(naip_ds.GetProjection())
clfds.GetRasterBand(1).SetNoDataValue(-9999.0)
clfds.GetRasterBand(1).WriteArray(clf)
clfds = None
print('Done!')
Create a confusion matrix to determine pixel accuracy
import numpy as np
import gdal
import ogr
from sklearn import metrics
naip_fn = 'C:/temp/naip/clipped.tif'
driverTiff = gdal.GetDriverByName('GTiff')
naip_ds = gdal.Open(naip_fn)
test_fn = 'C:/temp/naip/test.shp'
test_ds = ogr.Open(test_fn)
lyr = test_ds.GetLayer()
driver = gdal.GetDriverByName('MEM')
target_ds = driver.Create('', naip_ds.RasterXSize, naip_ds.RasterYSize, 1, gdal.GDT_UInt16)
target_ds.SetGeoTransform(naip_ds.GetGeoTransform())
target_ds.SetProjection(naip_ds.GetProjection())
options = ['ATTRIBUTE=id']
gdal.RasterizeLayer(target_ds, [1], lyr, options=options)
truth = target_ds.GetRasterBand(1).ReadAsArray()
pred_ds = gdal.Open('C:/temp/naip/classified.tif')
pred = pred_ds.GetRasterBand(1).ReadAsArray()
idx = np.nonzero(truth)
cm = metrics.confusion_matrix(truth[idx], pred[idx])
# pixel accuracy
print(cm)
print(cm.diagonal())
print(cm.sum(axis=0))
accuracy = cm.diagonal() / cm.sum(axis=0)
print(accuracy)